Bad data quality or lack of data utilisation: how to avoid a 12% revenue hit
Chloé Caron7 min read
Data comes from an endless list of sources, whether it be active and searching (e.g. use of sensors, collection of user data) or passive and an ‘added bonus’ (e.g. product sales, customer service emails). Data tells us a lot about our product, both what we are doing right and wrong in the eyes of the users. However, US companies are losing around 12% of their revenue due to bad data, according to an Experian report. How is that possible? Data is a great asset when it comes to decision-making and growing your company, but bad quality can also be damaging,
Most of the time, you use this data to track your ‘success criteria’ and be able to celebrate the fact your product is doing well (or that you need to re-evalute your product if it is doing less well). But this only scratches the surface of what data can actually do. So, how can you make your data work more? And, if you don’t, what are you losing out on?
Why do we care about data?
Let’s start with the second question. Why do we care about data? We know our product is doing well, so we’re on the right track, no?
Yes, that’s true, but is ‘on the right track’ really going as far as you can push it? You may still be growing, but without using your data, you are likely losing out on much faster growth.
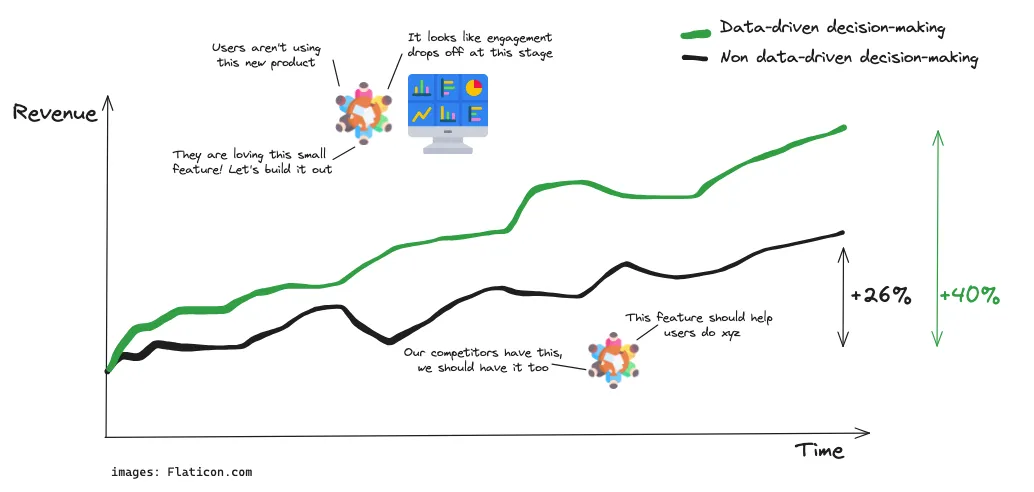
Data is important to help you stay ahead of the curve and grow your company. This missed revenue opportunity comes from multiple sources:
- Competitive disadvantage - data shows trends, trends help you stay ahead of the market. Without making use of this, it is easy to have a suboptimal understanding of your user behaviour and fall behind as the market continuously evolves
- It is difficult to quantify this value, as it depends on your industry but having a competitive advantage means an increase in market share, customer loyalty, pricing power, etc.
- Unguided Decision Making - similarly to the point above, data enables you to make decisions with confidence as it is backed by concrete, real-life information. Decision-making without evidence can be a road to failure
- According to BARC, organisations have attributed an 8% in revenue increase and a 10% in cost reduction to analysing big data
- Using a concrete example, in this article we see how using data helped to guide development of a healthcare app and increase user acquisition by 15%
- Bad data causing critical situations are also sadly common. Just take the 2008 financial crisis which was partially fuelled by:
- Risky mortgages given based on inaccurate information
- Risky financial products where the data used to analyse the risk was inaccurate
- Trust issues in financial institutions since they didn’t understand the risks of deals they were making because of incomplete or unreliable data
- Security and Compliance - collecting user data implies following legal requirements. Not being aware of this can have severe consequences, for both your finances (through legal prosecutions) and your reputation
- 10% of organisations are reported to have been fined due to data issues
- GDPR fines start at 2% of your companies annual revenue (or 10€ million), although this depends on where you are based
- Non-compliance costs 2.71 times the cost of meeting the compliance requirements
Being at a competitive disadvantage and unguided decision-making are closely related as they both stem from a lack of use or a misuse of data available to you. The common causes are:
- Lack of Data Processing - a spreadsheet with hundreds of columns and rows of raw numbers can be both mind-numbing and ineffective. Without processing your data into valuable figures, key stakeholders will not see the value it brings, nor will it empower you in making concrete and informed decisions
- Between 60% and 73% of all data within a company goes unused
- Bad Data Quality - incomplete or inaccurate data sets can lead to both misguided decisions and loss of trust in the data available
- According to an Experian report, an average company in the US loses around 12% of its total revenue due to bad data, costing the US economy around $3.1 trillion dollars every year.
Most companies already have data available to them and are simply not using it in an effective manner. Processing data has multiple stages to it, starting from data collections/data sources all the way up to data visualisation. Each of these stages warrant multiple articles to themselves. In this section let’s focus on two keys situations based on the issues we’ve raised: lack of data processing and bad data quality.
How to get started with data processing when starting from nothing?
To give an overview, this is what a classic stack might look like. Note that there are lots of tools out there which can do multiple parts of a data flow (e.g. transformation + storage) and that the stack can be split in different ways. The following diagram is one interpretation of the flow.
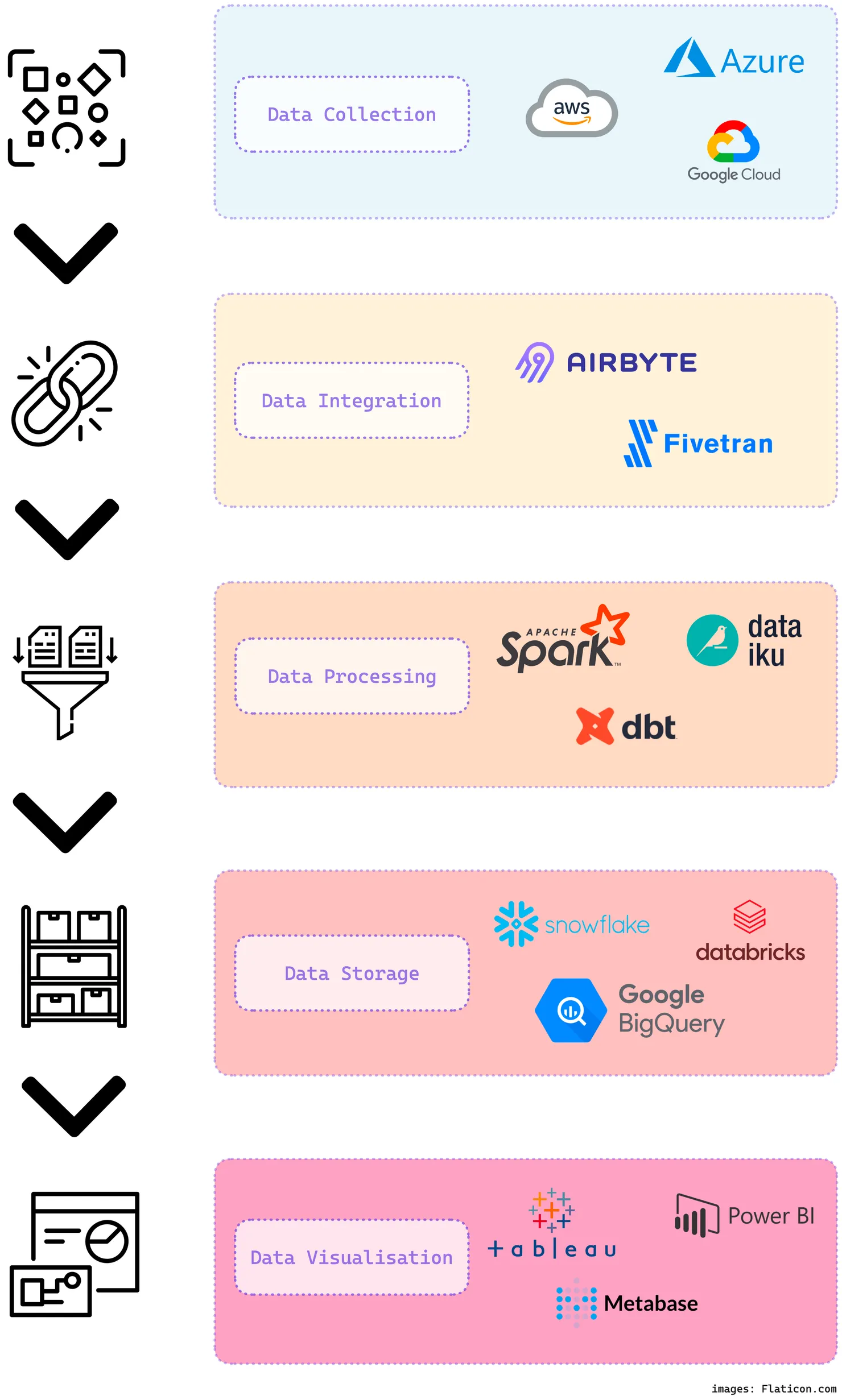
What if you are starting from scratch? How do you start using your data if you are starting from zero? There are multiple options available to you, but it all depends on your budget, tools that you currently use, what you want to use your data for, etc.
If you are not budget limited, then starting with a tool which allows you to handle multiple data stages in one with minimal up-skilling is the best place to start. Tools such as Snowflake and Databricks are examples of both popular and well-maintained platforms. There are also some open-source alternatives that you can use such as Dremio.
If you are budget limited, you might want to consider creating your data flow using open-source alternatives. Remember that you will still need to use a storage solution which will all be, as far as I know, paid solutions. For examples of open-source tools you have: Airbyte for data integration, dbt for data transformation and Metabase for data visualisation.
A few things to consider:
- Depending on the Cloud provider you use (e.g. GCP, AWS), they often have in-house tools which may make your life easier from an integration point of view. For example, using AWS you can have:
- S3 buckets for data storage
- AWS DMS for data integration
- AWS Glue for data transformation
- AWS Redshift for cloud data warehouse
- AWS Athena/Quicksight for analytics and visualisation
- If you already have part of the flow (e.g. data storage and data processing) and are looking at completing your current flow, it is good to consider which tools integrate best with your current stack.
How to handle bad data quality?
Identifying where your bad data quality is arising is a challenge all on its own. There are multiple tools out there that can give you better visibility on your data, such as Sifflet (paid) and Elementary (open source). This article by Lucie Martin gives you an insight into the use of Sifflet and this one by Etienne Gacel takes a look into Elementary. They both allow you to deep-dive into specific data quality issues that have been identified in order to pin-point the source. Some solutions, like Sifflet, will have a predetermined set of data quality checks that you can implement as well as allowing you to add your own set of rules.
After you’ve found the source of the bad data quality, you can implement a new stage in your pipeline to transform your data and ‘clean’ any sources of bad data. The additional transformation you implement on top of your current pipeline will depend on the issue you spot and should aim to correct any bad data quality. There are multiple key sources of bad data, some of which are illustrated below:
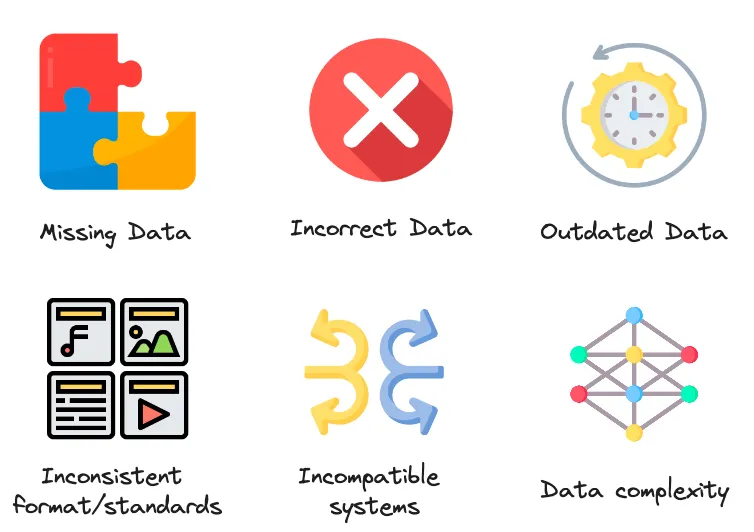
By elaborating on your data transformation stage, you can guard against these sources and improve the quality of your data.
Conclusion
Overlooking your data strategy can negatively impact your revenue growth through bad data quality or lack of a complete data processing pipeline. Data Engineering is a well-established field with both paid and open-source tools being available for each step of the data pipeline. By adopting this strategy, organisations starting from scratch can embark on a transformative journey, unlocking the full potential of their data and ensuring a competitive edge in the data-driven landscape.
If you are interested in building out your data solution, don’t hesitate to reach out or contact us through the Theodo website!
Feel free to reach out to me on X (Twitter) @ChloeCaronEng!