Prevent AWS from Reading Your Step Functions Data
Axel Fournier6 min read

AWS Step Functions is the perfect tool to handle long-running, complex or business-critical workflows such as payment or subscription flows. However, a naive implementation could put sensitive data at risk.
What is AWS Step Functions?
AWS Step Functions is an Amazon cloud service designed to create state machines to orchestrate multiple Lambda functions, branching logic and external services in one place. It presents most of the advantages of the serverless services: the scaling is immediate and the pricing is based only on the computing time and the number of step transitions.
The state machines can be defined directly in the AWS Console with a JSON configuration and you directly have a graph representation of your workflow.
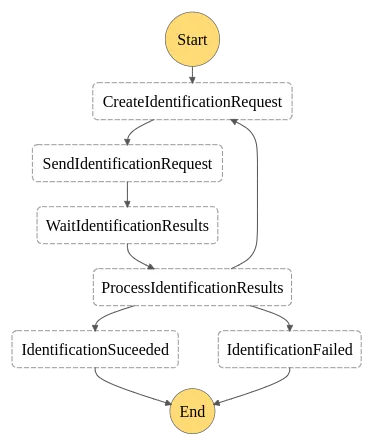
At Theodo, we use Serverless as our framework with the Step Functions plugin to write our AWS Lambda functions, define our resources (DynamoDB and Queues) and setup AWS Step Functions and the state machines directly in our codebase.
Example: an identity verification workflow with Step Functions
The previous picture shows an identification verification workflow. It is a piece of a bigger validation flow for banking applications.
What it does is request an identification URL to a third-party system, send this link by text message to the applicant and wait for them to complete the identity verification. When it is done, the third-party system calls a webhook, which restarts the state machine and either triggers a retry, sends a rejection email, or continues the global validation process.
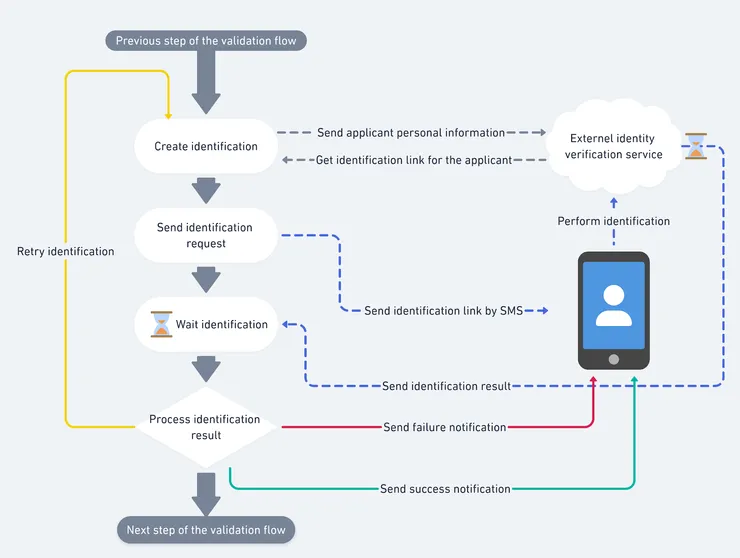
To perform all of those actions, sensitive information will flow through the inputs and outputs of the state machine steps:
- 👤 Personal information from the applicant which are sent to the third-party service to check his/her identity
- 📱 The phone number of the applicant to send the SMS
- ✉️ The email address of the applicant to send the mail
- ✔️ The result of the identity verification
Problem: we are exposing sensitive data
With this implementation, we see that sensitive data flow through the inputs and outputs of your state machine directly.
state-machine.yaml
----------
SendIdentificationRequest:
Type: Task
Resource: arn:aws:states:::lambda:invoke
Parameter:
FunctionName:
Fn::ImportValue: ${self:provider.stage}-sendSMS-Function-arn
Payload:
creditApplicationId.$: $.creditApplicationId
creditApplicant.$: $.creditApplicant
phoneNumber.$: $.phoneNumber
message.$: $.smsBody
ResultPath: $.identificationSMS
Next: WaitIdentification
The problem is: nowadays, most DevOps engineer, developers and even some product managers with access to AWS and can see that information. Furthermore, AWS Lambda dumps are stored in an S3 bucket which is not encrypted with the default configuration. Any malicious access to your AWS stack could leak sensitive information far more easily than by corrupting your database for example. The more you spread sensitive information between multiple services, the more you put yourself at risk. Finally, as it is stated in AWS documentation:
Any data that you enter into Step Functions or other services might get picked up for inclusion in diagnostic logs.
Depending on your data classification or threat model, this could be totally unaceptable. With that in mind, you may completely dump AWS Step Functions, or you may try to find a solution because the tool is still awesome and perfectly suits your needs!
Our solution
To prevent leaking sensitive information, we need to clean every step function input and output. Here are three ways of doing it:
- Configure Step Functions to log in CloudWatch Logs instead and set a low expiry date. This is the easier solution but it still exposes logs for a short duration, and you lose any chance of retrieving old execution informations later.
- Keep the data in the input and output but encrypt and decrypt it between each step. This one is a bit more complex but you only need to use an encryption key in your lambdas. However, you are still exposing encrypted data, which can be insufficient for some critical sectors, such as health or defense.
- Never transmit sensitive data between steps and retrieve it directly during their execution. This solution requires more services to work and thus more things that could fail. However, it is the more secured and allow permanent recovery of logs.
Second and third solutions also requires break-glass processes to allow developpers to legitimately access log data, for debugging or support matters.
Considering everything, we prefered to implement the last solution because we wanted to keep our sensitive data in a single safe spot, where we put a lot of attention to the security. Also, we were already using secured AWS DynamoDB encrypted with external KMS keys for the waiting tokens of our lambda functions. Thus, we decided to create a new table to store sensitive data between steps.
We configured it like below.
resources.yaml
----------
StepSentiveInputTable:
Type: AWS::DynamoDB::Table
DeletetionPolicy: Retain
Properties:
TableName: step-sensitive-input-table
AttributeDefinitions:
- AttributeName: sensitiveInputId
AttributeType: S
KeySchema:
- AttributeName: sensitiveInputId
KeyType: HASH
BillingMode: PAY_PER_REQUEST
PointInTimeRecoverySpecification:
PointINTimeRecoveryEnabled: true
SSESpecification:
SSEEnabled: true
SSEType: KMS
KeyId: hsm-key-id
We were already using DynamoDB from our lambdas to save our waiting task tokens and we chose to add another table to save sensitive data between steps. Furthermore, on AWS, you can choose to save the encryption keys of your DynamoDB tables outside of AWS, which was a big plus for us.
To avoid repeating ourselves, we coded a wrapper that we use on all our lambdas. It does the following things:
After the return of the lambda, the wrapper:
- Looks for sensitive data keys in the output, remove them and build an object with that information
- Save the sensitive data objects in a dynamo entry
- Add the id of the new dynamo entry under a “sensitiveData” key in the output
Before the execution of the main lambda function, the wrapper:
- Looks for “sensitiveData” keys in the input
- Retrieve the content at the given IDs
- Replaces the “sensitiveData” keys with the resulting object in the input
// encryption-wrapper.ts
export default (lambdaHandler: LambdaHandler): LambdaHandler => {
const decryptHandler = async (event: any) => {
const decryptedInformation = await getSensitiveData(event.sensitiveInputId);
return lambdaHandler({ ...event, ...decryptedInformation });
};
return async (event: any) => {
const clearOutput = await decryptHandler(event);
const sensitiveInputId = await storeSensitiveData(clearOutput);
for (const sensitiveKey of sensitiveInputKeys) {
delete clearOutput[sensitiveKey];
}
return { sensitiveInputId, ...clearOutput };
};
};
Last of all, we needed to encrypt the first input at the start of our state machine from the API to finally secure our users information all the way!
Takeways
- Take care about what information you have in your lambdas and state machine events on AWS
- Always think twice about the data you put in your logs
- Spread your secrets and security implementation in as few services as possible
- Use a wrapper if you want to repeat behavior in multiple lambda functions.
Thank you very much for reading my article. Feel free to comment, ask for implementation details, and feel free to share the problems that you encountered with AWS Step Functions.