Get Straight to MVP using Chatbots (and Algolia) (Part 2)
Jérémy Gotteland6 min read

In my first article, I talked about creating an MVP with a Chatbot and showed an example with Cinebot
But getting the bot up and running wasn’t enough.
It needed to be able to search complex data from text and location queries sent by the user through Messenger.
So I started to look for a cheap and flexible solution to store and retrieve data. At around the same time I heard about Algolia, a French company providing exhaustive search capabilities through a SaaS platform, and decided it was worth trying out.
In this article I’ll explain how I tuned Algolia to provide relevant search for my users in just a few hours.
Introduction
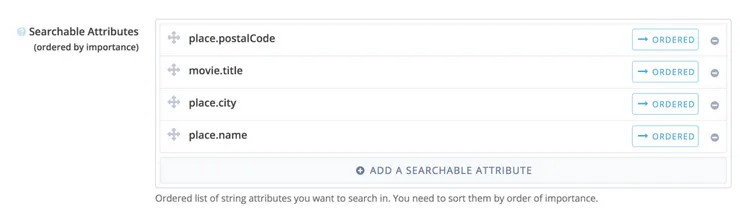
Algolia acts as a data store, so I will fetch the screenings data daily using cron jobs and upload it there.
This will allow my chatbot to use Algolia’s exhaustive search capabilities to return relevant data.
Here is a diagram to show what the architecture of the project looks like:
💵 Algolia Free Plan: Discovery
Algolia Free Plan includes 10,000 records and 100,000 operations (an operation can be adding a record or querying the database).
It’s quite limited but enough for my MVP: creating a chatbot to help Parisians find showtimes in their city.
For approximately all the Paris and surrounding area, I have 2,500 records per day.
Which means ~30x2,500 = 75,000 operations per month, which fits into the free plan.
N.B: In order to use Algolia Free Plan, you must put their logo somewhere in your product
Creating an index and getting the keys 👆
First you need to go to https://www.algolia.com/explorer/indices and to create a new index (the equivalent of a MongoDB collection, that will hold your records).
Give it the name you want, I called mine cine_seances.
Then head to https://www.algolia.com/api-keys to get your Application ID and Admin API Key.
Then we’re ready to roll.
Data Description
The searchable items are releases: they represent all the screenings for a given movie in a given cinema, on a given day:
{
"place": {
"name": "Le Cinéma des Cinéastes",
"city": "Paris 17e arrondissement",
"postalCode": "75017",
},
"movie": {
"title": "Moonlight",
"language": "Anglais",
"vo": true,
"posterUrl": "http://images.allocine.fr/pictures/17/01/26/09/46/162340.jpg",
"pressRating": 4.18421,
"userRating": 4.07561159,
"url": "http://www.allocine.fr/film/fichefilm_gen_cfilm=242054.html",
"is3D": false,
"releaseDate": "2017-02-01",
"trailerUrl": "http://www.allocine.fr/video/player_gen_cmedia=19565733&cfilm=242054.html"
},
"date": "2017-02-24",
"times": {
'13:15': 'https://tickets.allocine.fr/paris-le-brady/reserver/F191274/D1488024900/VO',
'17:30': 'https://tickets.allocine.fr/paris-le-brady/reserver/F191274/D1488040200/VO',
'19:45': 'https://tickets.allocine.fr/paris-le-brady/reserver/F191274/D1488048300/VO',
'22:00': 'https://tickets.allocine.fr/paris-le-brady/reserver/F191274/D1488056400/VO'
},
"_geoloc": {
"lat": 48.883658,
"lng": 2.327202
}
}
Updating the data
Algolia provides clients for many languages which means you can work with the language of your choice.

I went with Javascript since my bot is developed in Javascript. Hence, I needed to install two Javascript packages and add the corresponding two lines on top of every .js file where I’ll use Algolia:
npm install --save algoliasearch
npm install --save algoliasearch-helper
const algoliasearch = require('algoliasearch');
const algoliasearchHelper = require('algoliasearch-helper');
Uploading fresh data
The clients allow for batch uploading of JSON arrays, which is quite convenient.
However two days of screenings are contained in a 3.4Mb JSON array, and batch uploading the entire array often timed-out.
A solution is to upload small chunks of 100 screenings. With asynchronous Javascript, uploading does not take more than 5 seconds.
const algoliaIndexName = 'cine_seances';
const algolia = algoliasearch(APP_ID, ADMIN_API_KEY, {
timeout: 5000
});
const showtimes = require('./showtimes.json');
const _ = require('lodash');
const index = algolia.initIndex(algoliaIndexName)
_(showtimes).chunk(100).forEach((chunk) => {
index.addObjects(chunk, function(err, content) {
// ...
});
});
Deleting old data
Since the free plan can only contain two days worth of data, every upload of a new batch means clearing all the records currently held in the database before uploading new ones.
index.clearIndex(function(err, content) {
// OMG TOTAL WIPEOUT 😱
_(showtimes).chunk(100).forEach((chunk) => {
index.addObjects(chunk, function(err, content) {
// 💯
});
});
});
Algolia Configuration
Once the data is in there, it’s very simple to select the fields that will be searchable through Algolia, and the order in which they should be displayed to the user. It all happens in the index dashboard at https://www.algolia.com/explorer#?index=cine_seances
Searchable Attributes
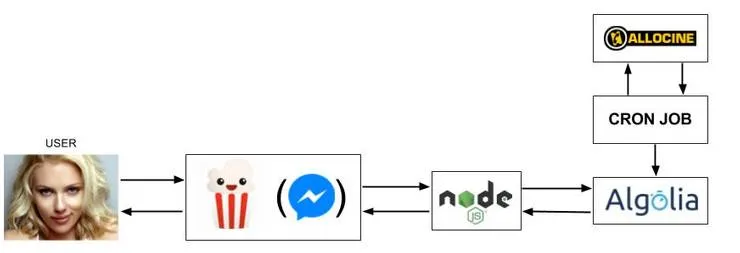
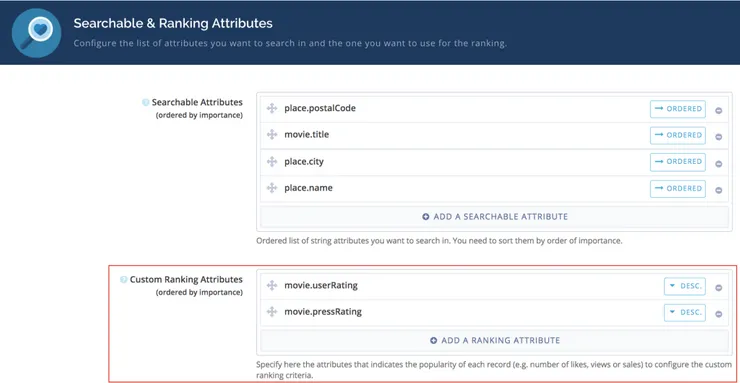
After experimenting a bit, I found out the following order for the attributes that were important in the search:
- Postal code
- Movie Title
- City
- Theater Name
All that is needed is to add the attributes through the interface and order them in the way I want them to be prioritized.
Enabling Geolocation 🌏
A key feature I needed in the bot was the ability for the users to send their location and discover screenings around them.
Facebook Messenger allows you to prompt the user for his location, which can be useful as a fallback when the user does not understand how to talk to your chatbot.
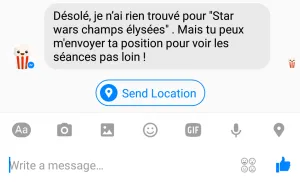 When no screening is found based on the query, the bot prompts the user to send its location instead.
When no screening is found based on the query, the bot prompts the user to send its location instead.
And then getting the location back from the message:
if(event.message && event.message.attachments) {
const attachment = event.message.attachments[0];
if(attachment.type === 'location') {
const location = {
'latitude': attachment.payload.coordinates.lat,
'longitude': attachment.payload.coordinates.long,
}
}
}
Enabling geolocation search is simple with Algolia as you only need to add a _geoloc field to your records and enable Geosearch in the Dashboard:
{
...
"_geoloc": {
"lat": 48.883658,
"lng": 2.327202
}
}
Then by adding a query parameter aroundLatLng, you will get the results sorted based on distance.
You even get the distance in meters to the cinema, which you can then display to the user.
algoliaHelper.setQueryParameter('getRankingInfo', true);
algoliaHelper.setQueryParameter('aroundLatLng', `${location.latitude},${location.longitude}`);
algoliaHelper.setQuery('').search();
algoliaHelper.on('result', (result) => {
const hits = result.hits;
console.log(`Closest result is ${hits[0]._rankingInfo.matchedGeoLocation.distance} meters away.`)
});
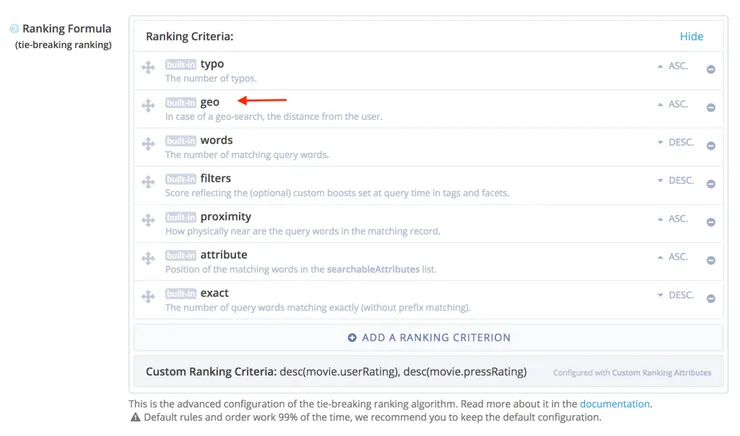
Custom Ranking ⭐
Since I also had the information about the movie ratings, I wanted the results to be displayed in an order based not only on the proximity, but also on the quality of the movie.
To do so I defined Custom Ranking Attributes just below the searchable-attributes in the console, and Algolia sorts it out by itself.
Faceting for Same Day Retrieval
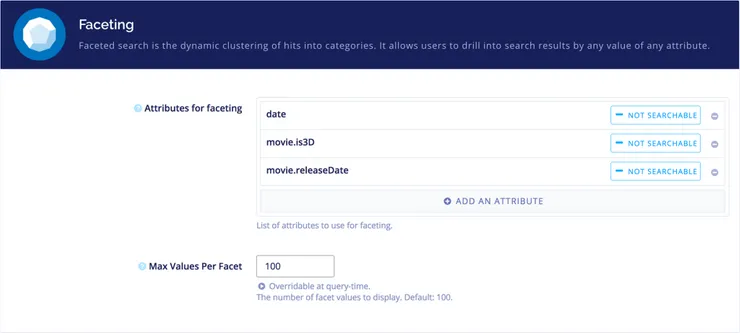
After setting up the ordering of results, I wanted to retrieve only the screenings for the date of today.
To do so I used faceting which allows me to index a field with a limited number of discrete values to make them easily searchable.
By faceting the date field, I was able to query all the showtimes for today’s date.
this.algoliaParams = { facets: ['date'], hitsPerPage: 10 };
const algoliaHelper = algoliasearchHelper(this.algolia, this.algoliaIndexName, this.algoliaParams)
algoliaHelper.addFacetRefinement('date', today);
algoliaHelper.setQuery('La La Land').search();
algoliaHelper.on('result', (result) => {
const hits = result.hits;
console.log(`${hits.length} showtimes for La La Land today.`)
});
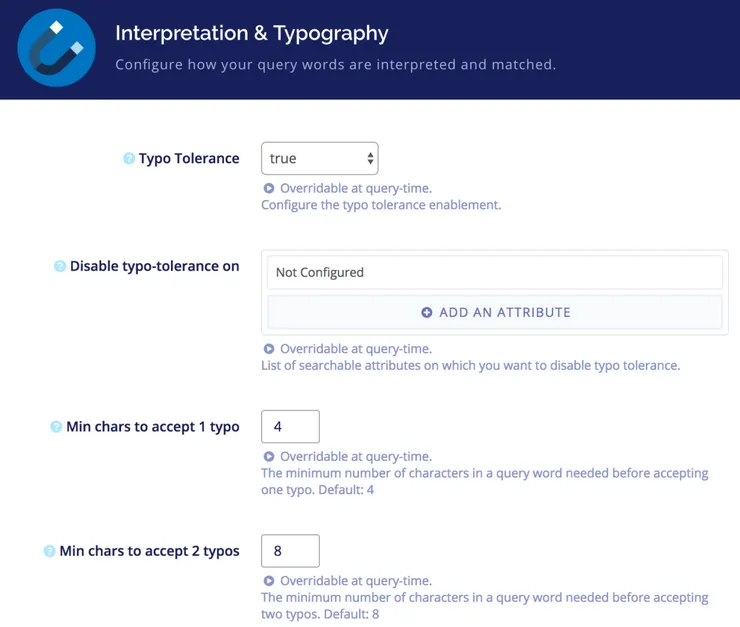
Typo Tolerance
With Algolia you can also fine tune typo-tolerance on every field: if it should be enabled or not, the minimum number of characters before accepting 1 or 2 typos, and if stop words should be removed for example.
For a more exhaustive list, scroll down to this section on your index page.
That’s it, folks!
In a few hours, I was able to get Algolia configured to perform complex queries on my dataset and provide fast and relevant search to my users based on what their textual query as well as their location if they wish to share it.
I’d definitely recommend Algolia to anyone who wants to perform search on a slightly complicated dataset without the overhead of setting up an in-house solution.
However, getting more space and operation capacity comes at a cost: 49,9$/month for Starter Plan with 100’000 records and 1’000’000 operations. So you’d better have a product that makes money 💷